NIH Stroke Scale Calculator – Instantly Evaluate NIHSS
The NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) Calculator is a clinical tool used to assess the severity of a stroke by evaluating neurological deficits such as consciousness, vision, movement, and speech. It helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment and monitor patient progress. Accurate NIHSS scoring supports timely intervention and improved stroke outcomes.
NIH Stroke Scale Calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
What Is Stroke?
Stroke, a medical disorder in which insufficient blood flow to the brain results in cell death, happens when something limits blood supply to part of the brain or when a blood artery in the brain breaks. Both freeze certain brain functions in their tracks.
Common signs and symptoms might include difficulty speaking or recognizing, dizziness, or a loss of vision on one side of the body. On one side of the body, they may also cause trouble moving or feeling. Symptoms and indicators of a stroke typically emerge quite fast.
What Is the NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS)?
The NIH Stroke Scale, which was created via research funded by National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), assists medical professionals in determining the severity of a stroke in patients. This tools includes 15 components that helps in checking brain functioning. It helps in evaluating concentration, emotions, vision, speech and movement. Used by the doctor to evaluate the damage the brain may have and also to see if the condition of the patients is getting better or worse.
Why Is the NIH Stroke Score Important?
The patients go through the test that is done under the supervision of health-care provider. They ask them the questions and do various physical and mental tests. By having the patient respond to questions and complete a number of physical and mental tests, doctors utilize the NIH Stroke Scale to evaluate neurological function and disabilities. The NIHSS has proven that is an excellent tool for the prediction of patients outcome. There are to main baseline of score that predict the continuity of the patients. If the score is greater than 16 there is high risk of death an under the a score of 6 are high chances of good recovery.
NIHSS Scoring Breakdown
The NIHSS consists of 11 items, each of which is scored between 0 and 4 for a particular skill. In general, a score of 0 for each item shows normal function in that particular skill, whereas a higher number denotes some degree of disability.
Components of NIHSS:
- Level of consciousness
- Horizontal eye movement
- Visual field test
- Facial palsy
- Motor weapon
- Engine leg
- Limb ataxia
- Sensory
- Language
- Speech
- Extinction and inattention
Evaluation of score
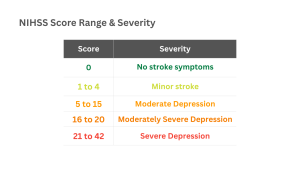
When to Use the NIH Stroke Scale Calculator ?
This is tool is used by the health-care professionals to evaluate the severity of the stroke in emergency cases. Helping in the prediction of the patient outcome, monitoring the progress and giving the right treatment are some of key features of this tool. The scale is used in many studies to ensure and guarantee regular stroke evaluation, also the moment that the patients comes for the first time to evaluate the severity of their stroke and during the time in hospital to track their changes during the time.
NIHSS score should be used along with medical examinations beside the fact that offers very useful insights. Correct use of this score requires a good training to make the right examination. For the purpose of predicting recovery and directing treatment choices, the first score is particularly crucial.
Limitations of NIHSS
We have talked about all the helpful thing that the tool have in determining the severity of stroke but it also has some limitations. It might ignore or underestimate strokes the front part of the brain (posterior circulation), such as brainstem and cerebellar strokes, but it performs best for strokes in the front of the brain (anterior circulation). Also, diagnosing cognitive issues like dementia and minor strokes it faces troubles. These weaknesses might allow the tool to neglect some symptoms the patients might have that may have an impact on the on the evaluation and treatment decisions.
Explore More Helpful Health Tools
Our website is here to build easy-to-use tools that motivate people to make healthier life decisions and take charge of both their physical and mental well-being. From tools like the NIH Stroke Scale Calculator to a wide range of other health calculators, our platform is designed to support your wellness journey.
Below you can explore a few of our tools and more tools are just a search away. If there is a specific test or calculator you need and can’t find, feel free to contact us. We’re always happy to develop new tools that benefit everyone.
Child Pugh Score Calculator – Instantly Calculate Cirrhosis Severity
Helps evaluate liver function and cirrhosis prognosis based on key clinical indicators.
General Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) Calculator
A quick and effective tool to assess the severity of generalized anxiety symptoms.