FENa Calculator – Instantly Check Fractional Excretion of Sodium
The FENa Calculator helps assess kidney function by measuring the fractional excretion of sodium. It is particularly useful in distinguishing between prerenal and intrinsic renal causes of acute kidney injury. Accurate calculation helps doctors in making timely and informed treatment decisions.
Disclaimer
This calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
What is Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)?
Acute Kidney Injury is an unexpected change in kidney function that is evaluated through reduced glomerular filtration rate (GRF) that is also a common indicator of acute kidney injury. Aki before was known as acute renal failure. Sodium, water, waste products and imbalance of electrolytes are all results of AKI. AKI is a complex medical condition that can have many different causes, such as exposure to nephrotoxic substances and ischemia damage.
This condition is common in patients that are hospitalized and especially in intensive care. To have a more precise result doctors use different evaluation standard like such as KDIGO, RIFLE, and AKIN, of which KDIGO is the most commonly used. Acute kidney failure can be detected in his early stages if start to see the sing like very low urine production or flow. Beside a low urine flow onother way to detect is blood testing.
Types of AKI: Prerenal vs. Intrinsic
Prerenal and intrinsic are the 2 main categories that acute kidney failure is divided into. The moment that kidneys are not receiving the right amount of blood flow, which can be caused by conditions such as heart failure, dehydration or sepsis, this is the moment that AKI occurs. If you catch it in early stages and treat it is commonly cured.
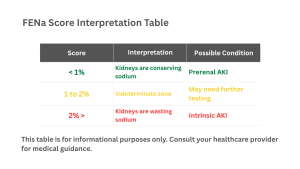
On the other hand, if you don’t catch in right time, it progresses and can result in intrinsic AKI, that damages directly the kidneys themselves. This kind of damage have an impact on the kidney filters, tubules, or surrounding tissue. The impacted areas may have results such as toxins, immunological disorders or infections. In more severe situations intrinsic AKI might result in chronic kidney injury. To separate this 2 conditions from each other is used test like the urine sodium and FENa , which is very helpful in evaluating them.
What is FENa?
Fractional excretion of sodium is the amount in percentange of sodium which is filtered by kidneys that than is released in the urine. This is not a test but is formula to calculate the blood and urine slat and creatine concentration. Both urine an blood samples are taken to the lab to examined because to make the calculation the results of both are needed.
This calculation can be important for the evaluation for acute kidney failure (AKI) on the factors for low urine excretion. If the evaluation indicates low fractional excretion which may indicate a reduction in effective circulating volume. Higher levels may indicate wasting of sodium and the reason may be to acute tubular necrosis or causes of kidney failure.
Formula of FENa

Why is FENa Important?
Fractional Excretion of Sodium is an essential tool used be the healthcare providers to determine the causes of acute kidney injury. This technique helps in finding the main reason that the problem occur like too little blood flow or damage inside the kidney. It helps doctors to give the best treatment such as providing fluids in situations that are prerenal.
This method measures the amount of sodium that is eliminated through the urine. When doctors calculate FENa and if the score is high indicated that kidneys are leaking sodium. Low score indicates that kidneys are attempting to keep it (prerenal). The results of the test always should be evaluated carefully because factors like diuretics and other drugs might impact the result.
Limitations of the FENa Test
Despite it can be used to determine the causes of acute kidney injury (AKI), the Fractional Excretion of Sodium have some significant limitations. Diuretics and some other medications have an impact and they increase the levels of FENa and leading to wrong results. Patients that may have other health problems like cirrhosis, heart failure, sepsis or chronic kidney diseases may have incorrect results from the test due to improper salt processing.
Also, some other conditions like rhabdomyolysis or contrast-induced kidney injury can also result in low score. In some cases like kidney function is only mildly affected or in non- oliguric AKI, the score is less dependable but in this cases for a more precise result is used FEUrea. Healthcare providers before taking the test they should have a clear understanding of the patients health condition and then interpret the test for best possible results.
FENa Score Interpretation Table
Explore More Helpful Health Tools
Our website is dedicated to creating tools that empower people to make informed life choices and take control of their physical and mental well-being. We offer a variety of health-related tools, such as the Fractional Excretion of Sodium Calculator, all designed to support your overall wellness.
Below, you’ll find some of our featured tools, along with many more just a quick search away. If you don’t see a specific test or calculator you need, feel free to contact us, and we’ll be happy to create it for the benefit of everyone.
Bishop Score Calculator
Quickly assess cervical readiness to predict the success of labor induction and vaginal delivery.
Serum Anion Gap Calculator
Instantly evaluate acid-base imbalances using serum electrolyte values for clinical insight.