CHA2DS2-VASc Score for Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Risk
The CHA2DS2-VASc Score is a clinical tool used to estimate the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. It evaluates factors such as age, heart failure, hypertension, diabetes, prior stroke, vascular disease, and sex. Accurate scoring helps clinicians make informed decisions regarding anticoagulation therapy to prevent stroke.
CHA2DS2-VASc Score Calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
The most common kind of cardiac arrhythmia that is treated is atrial fibrillation, which is an irregular and sometimes extremely fast heart rhythm (abbreviated as AFib or AF). When the heart beats abnormally, too quickly, or both, it is said to have an arrhythmia. The regular cycle of electrical impulses in your heart is disrupted if you have atrial fibrillation. This causes a rapid, erratic heartbeat and insufficient blood flow from your upper chambers (atria) to your lower chambers (ventricles).The condition raises the risk of heart attack, heart failure, and other issues that involve the heart.
Why Is Stroke a Concern in Atrial Fibrillation?
Stroke is concern because the risk of stroke is increased due to irregular heartbeats that affect blood flow to be poor. Because of an abnormal rhythm blood colts may start to develop in part of the heart that is the left atrial appendage. A clot that makes its way to the brain has the potential to prevent blood flow and result in a stroke. Strokes are three to five times more common in those patient with atrial fibrillation than in ones without it.
Strokes caused by AF are often more severe and they can result in significant long-term problems. Luckily, with the right care, such as taking blood thinners, many of these strokes may be avoided. The progress of modern medicine and healthcare has made it possible to prevent strokes through proper treatment, including medications like blood thinners, which have a strong impact in reducing stroke risk.
The Role of Risk Assessment in AF Management
Risk assessment is crucial for doctors managing atrial fibrillation (AF), as it helps predict the risks of stroke and bleeding and guides decisions about anticoagulation treatment. In the evaluation process various factors are taken into consideration so patients can be categorized into different groups to manage their health conditions better and to have personalized treatment.
There are some tools used by healthcare professionals to help them identifying for strike and bleeding risk. Two main one are CHA2DS2-VASc which helps in determining patients with higher risk of stoke and HAS-BLED score which assists in determining bleeding risk. This dual examination assists healthcare providers to weight the advantages and disadvantages of blood thinners thanks to this methods.
Regular check-up are crucial because they help in adjusting treatment because risk factor might change over the time. The best results are ensured when a good strategy is used, taking into account comorbidities, lifestyle, and changing clinical condition. Effective risk assessment usually results in more informed choices and better treatment for AF patients.
What Is the CHA2DS2-VASc Score?
Doctors use different tools and methods to make the to make the appropriate assessments to evaluate the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation patients, and one of them is the CHA2DS2-VASc score. This methods functions by taking into consideration different risk factors that will be shown below. To each of the components I added a ranging score from 0 to 2 points based on the condition of each factor. Doctors use the total score to determine a patient’s risk of stroke and if blood thinners are necessary to help avoid it. In order to ensure that patients receive the appropriate care based on their personal risk, this scoring system is essential.
CHA2DS2-VASc Score stands for (also the components of the calculator):
- C – Congestive heart failure
- H – Hypertension
- A₂ – Age ≥75 years
- D – Diabetes mellitus
- S₂ – Prior stroke, TIA, or thromboembolism
- V – Vascular disease (e.g., MI, PAD, aortic plaque)
- A – Age 65–74 years
- Sc – Sex (gender) category
Score Interpretation
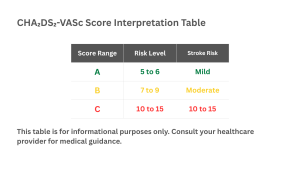
Benefits of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score
In the process of evaluating the risk of stroke in patients arterial fibrillation, CHA2DS2-VASc Score is a very useful tool that provides greater accuracy compared to the previous method, the CHADS2. It assists medical professionals in making specific decisions on the beginning of medication treatment for a patient. Combining other risk elements such as gender, age and vascular diseases it optimizes accuracy and assists to prevent unnecessary treatment.
In many healthcare clinics this scoring method is frequently supported because it is a reliable and uniform method. In certain cases, such as when implanted devices identify preclinical AFib, it can also be helpful in determining whether to take blood thinners. Overall, it improves safer, more individualized treatment and improves stroke prevention.
Limitations of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score
Beside being a frequently used tool in evaluating strike risk in patients, the CHA2DS2-VASc score has some limitations. In some patients that have low scores, it might not be accurate since it might underestimate their true risk of stroke. Various forms of arterial fibrillation or other illnesses like cancer, are not taken into consideration for a more precise score. Also, it might not be suitable for people with a history of bleeding or certain medical conditions. Doctors can use the score as a guide, but they should also combine it with their own experience and clinical judgment when treating patients.
Explore More Helpful Health Tools
Our website is here to create tools that help people to make better life choices and having your body and mind in control. We provide a range of health related tools like the CHA2DS2-VASc Score Calculator designed to support your well-being.
Below you will find a couple of them and much more that are just a search away . If you don’t find any specific test or calculator you’re looking for please feel free to contact-us so we can create it for everyone.
ABCD2 Score Calculator
Quickly assess the short-term risk of stroke following a transient ischemic attack (TIA) using the ABCD2 scoring tool. Ideal for early clinical decision-making.
NIH Stroke Scale Calculator
Use this calculator to instantly evaluate stroke severity with the NIHSS. Helps guide treatment decisions and monitor changes in neurological status.