FEUrea (Fractional Excretion of Urea ) Calculator
The Fractional Excretion of Urea (FEUrea) calculator helps assess kidney function, particularly in differentiating between prerenal and intrinsic renal causes of acute kidney injury (AKI). It provides a reliable alternative to the FENa test, especially in patients receiving diuretics, by evaluating how efficiently the kidneys excrete urea.
FEUrea Calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
Kidney Function Overview
The kidneys filter blood to eliminate waste and extra fluid, regulate pH and electrolyte balance, control blood pressure, and generate hormones including calcitriol and erythropoietin
Nephron is the functional unit that manages secretion, reabsorption, and filtration to preserve homeostasis. Having healthy kidneys is crucial for the human body becauses it maintains the overall body balance, due to this fact diagnosis diseases of kidneys in early stages is essential in preventing chronic kidney illnesses. They also play a key role in regulating blood sugar and supporting the body’s immune and metabolic functions.
Understanding Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is condition when an unexpected impairment of kidneys function that can occur over a period of hours or days. This condition can cause damage in other organs such as the heart, brain, and lungs. Also , it can cause waste and fluid to accumulate in the blood stream. It has to be treated on time to avoid serious complications. It can be caused by urinary tract problems (postrenal), direct kidney injury (intrinsic), or reduced blood supply to the kidneys (prerenal). Shortness of breath, nausea, disorientation, decreased urine output, swelling are some of the main symptoms. Untreated AKI might result in chronic renal disease or require dialysis in extreme cases, early medical treatment can usually restore kidney function.
Challenges in Diagnosing AKI
Acute kidney injury sometimes it can be difficult to identify in early stages due to the fact that it doesn’t show obvious symptoms. Doctors usually rely on tests like blood creatinine levels and urine output, but these can be slow to show changes and may be affected by other factors. Accurate urine measurement might be challenging at times, and currently there is not any available method or tool for monitoring kidney function in real time. To assist in identifying AKI earlier and more accurately, new and more sensitive diagnostics tools are being developed.
What is FEUrea?
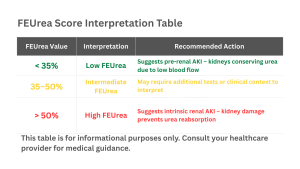
FEUrea (Fractional Excretion of Urea) is clinical method that helps to evaluate the kidney functions by taking into measurement how much filtered urea is released compared to reabsorbed. The test is a helpful tool for assessing acute kidney injury (AKI), and takes into evaluation process components such as urine and plasma levels of urea and creatinine. The accuracy can be impacted by factors like diuretic use. The score should always be interpreted together with the patient’s overall clinical picture.

Why FEUrea is Important
A useful non-invasive method for determining the origin of acute kidney injury (AKI) is FEUrea, which may be used to differentiate acute tubular necrosis from pre-renal azotemia. It is a useful method in particular for patients that are hospitalized or in severe conditions and compared to FENa, it maintains accuracy in patients on diuretics. This method has shown very good potential in difficult situations like cirrhosis, where it may have an impact in determining between intrinsic kidney damage and hepatorenal syndrome. It provides an understanding of tubular integrity in addition to its function in general AKI diagnosis.
Clinical Application of FEUrea
In patients with acute kidney injury (AKI), FEUrea is typically used for identifying acute tubular damage from pre-renal azotemia. It helps in separating conditions between pre-renal AKI, acute tubular necrosis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Also, it is useful especially for patients in diuretics that we talked before due to the fact that is more dependable than FENa. It also can also assist in identifying between temporary and permanent AKI in critically sick patients, enabling more focused treatment choices.
Limitations of FEUrea
FE Urea can be useful in diagnosing acute kidney injury (AKI), its interpretation has some limitations. In patients that have conditions such as sepsis, chronic renal disease, urinary tract infection, and diuretics affect how urea is handled, in this cases it can be less accurate. Results may also be impacted by other factors such as hunger, low-protein diets, or by medications. FE Urea’s overall diagnostic accuracy is limited by its clinical poor performance in identifying between transient and chronic AKI as well as between pre-renal and intrinsic AKI.
Tools to Support Your Health
Our website is here to create tools that help people to make better life choices and having your body and mind in control. We provide a range of health related tools like the FE Urea Calculator designed to support your well-being.
Below you will find a couple of them and much more that are just a search away . If you don’t find any specific test or calculator you’re looking for please feel free to contact-us so we can create it for everyone.
FENa Calculator
A tool to quickly assess kidney sodium handling and help differentiate causes of acute kidney injury.
Free Water Deficit in Hypernatremia
A calculation to estimate the amount of water needed to correct high blood sodium levels safely.