LRINEC Score for Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection
The LRINEC Score (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) is a clinical tool used to assess the risk of necrotizing soft tissue infections based on routine lab values. It helps healthcare providers identify high-risk patients early, enabling prompt intervention and improving outcomes.
LRINEC Score Calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
What is Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections (NSTI) ?
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections (NSTIs) are serious, rapidly spreading bacterial infections that damage muscle, fascia, and skin. If left untreated, they can cause sepsis, tissue loss, systemic poisoning, and sometimes even death. Some of the symptoms are usually presented with severe pain, quick spread of swelling and redness, and systemic disease.
Main causes include different type of bacterial infections that often occur from small injuries that contain bacteria such as streptococcus, staphylococcus, and anaerobes. Early diagnosis and immediate treatment are very important. Patients need urgent surgery to remove dead tissue, strong antibiotics to fight the infection, and care from a team of healthcare providers. Even with modern treatment, these infections still have a high risk of death and serious complications.
Challenges in Diagnosis NSTI?
Diagnosing NFTI can be difficult due to their confusing symptoms. Pain is typically far worse than how the skin seems, and patients may feel bad before any changes show up on their skin. In some cases there are no visible skin symptoms, and this lead to misdiagnosis that is common and causes the treatment to be delayed. Imaging may not always provide an clear evaluation and other disease like sepsis or diabetes problems have their impact on the imaging. The best way to find NSTI early is to stay alert for it, trust clinical judgment, and, if needed, do surgery quickly without waiting.
Importance of Early Detection of NSTI
Early detection of NSTIs is essential to improve recovery and saving lives. If the healthcare providers act quickly and do immediate surgery the risk of death is lowered, prevents amputations and minimizes the chances of complications like organ failure or sepsis. Also, early treatment has less extensive surgical intervention and better long-term results.
Sing that may be very difficult to deal with like severe pain that is out of proportion or skin changes like blisters or changed skin color are sing that may help doctors to act more quickly. Because early signs can be hard to spot in some cases, doctors need to stay alert and treat it right away when NSTI is suspected.
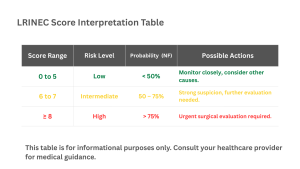
What is the LRINEC Score?
The LRINEC Score is a tool doctors use to help detect necrotizing fasciitis a dangerous infection in the skin, by examining the results of standard blood tests. It examines six test results: creatinine, salt, glucose, hemoglobin, white blood cell count, and CRP. LRINEC score assists healthcare providers in identifying early signs and guiding appropriate treatment, even that it isn’t ideal and sometimes it can miss the infections and depending which body area is affected it may act differently. Doctors may make faster examination and guiding appropriate treatment, by combining lab results with careful clinical examination. Aa a tool used for early examination, the LRINEC score may improve the patient outcomes and reduce complications from the infection.
Parameters of the LRINEC Score
• C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
• White Blood Cell count (WBC)
• Hemoglobin (Hb)
• Sodium
• Creatinine
• Glucose
Clinical Use of the LRINEC Score
Doctors can detect NSTI early and differentiate them from less serious infections like cellulitis or abscesses with the use of the LRINEC Score. Clinical choices are guided by the analysis of laboratory data, including creatinine, salt, glucose, hemoglobin, white blood cell count, and CRP. Early diagnosis, risk assessment, and quick management like doing emergency surgery when is necessary are all supported by the LRINEC score. It should be used in combination with clinical examination and imaging, not as an single diagnostic tool, even if it improves patient outcomes by lowering complications and death.
Advantages of the LRINEC Score
LRINEC Score is based on standard laboratory testing, it is easy to use and cost-effective. It supports healthcare providers in classifying patients according to risk level, identifying necrotizing fasciitis early, and determining it from less severe diseases. This allows for quick actions, such as emergency surgery when it is necessary. By helping doctors find the infection quickly and treat it in time, it leads to better recovery, fewer serious problems, and a lower chance of death. It is also a useful tool for directing treatment choices due to its predictive value.
Limitations of the LRINEC Score
The LRINEC Score is a helpful tool, but it has some limitations. Cases may go unnoticed because of the low sensitivity, particularly in the early stages of necrotizing fasciitis. Often it can perform poorly in emergency rooms and it may not properly check out the condition on its own. Also, in different populations the accuracy of the score may differ and misses crucial clinical indicators and imaging. Its reliability as a stand-alone diagnostic tool has been reduced since it may result in false positives for cellulitis and false negatives for necrotizing fasciitis.
Take Control of Your Health with More Tools
Our website is here to provide easy-to-use tools that help you make healthier life choices and take better care of your body and mind. We offer a variety of health calculators, like the LRINEC Score Calculator, to support your well-being.
Below you’ll find some of our tools, and many more are just a quick search away. If you don’t see the test or calculator you need, feel free to contact us—we’ll be happy to create it for you and others.
Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT)
A clinical tool that measures pain in critically ill patients who cannot self-report, based on behavioral cues.
Free Water Deficit in Hypernatremia
A calculation used to estimate how much water the body is missing in patients with elevated sodium levels.