Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT)
The Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) is used to assess pain in non-verbal or critically ill patients in intensive care settings. By evaluating facial expressions, body movements, and ventilator compliance, it helps healthcare providers manage pain effectively and improve patient comfort.
This calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
Pain in Critical Care
In the intensive care unit, pain is a common and sometimes ignored issue that can be brought on by operations, chronic illnesses, immobility, psychological suffering, or withdrawal. Pain can slow recovery, create anxiety or confusion, and lead to health issues if left untreated. Patients may not be able to express their feelings or communicate, making examination hard. In order to keep patients comfortable and speed up their recovery, good pain management include periodically evaluating pain, determining where it comes from, treating it first, and combining pain medication, sedation, and support.
Challenges in Assessing Pain
In young people, the elderly, or those with cognitive or linguistic problems, pain is personal and hard to accurately measure. Evaluation can be challenging since behaviors, culture, and family all influence how pain is expressed. Doctors may face difficulties due to busy workloads, limitations in training or not having the right tools to measure, and this leads to making the wrong evaluation. It becomes more difficult to distinguish pain from anxieties or other forms of discomfort, which makes regular effective care difficult. Determining the pain in accurate way is very essential for giving the right treatment and improve their comfort and recovery.
What is CPOT?
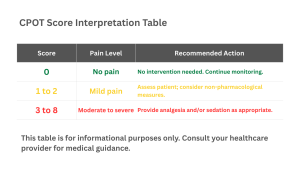
In critical care units, patients who are unable to talk, such those on ventilators, have their pain levels measured using the Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT). This tools uses for 4 factors to measure the pain level that are facial expressions, body movements, muscle tension, and either how well a patient works with the ventilator or their vocal sounds if not intubated. The total score ranges from 0 to 8 points, each of the factors is evaluated from 0 to 2 points based on the answer.
If the score is high it indicates also that the pain level is high. CPOT pain scale is essential due to the fact that helps healthcare providers to identify and deal with pain in very sick patients. Even in cases where the patients are unable to speak to describe the pain CPOT scale is crucial. This improves patient recovery and makes pain treatment safer and more reliable.
Purpose of CPOT
The CPOT’s primary goal is to support doctors in identifying and evaluating pain in patients who are too sick to talk for their condition. In this situations it ensures that the patients gets the appropriate medical attention and comfort and providing to doctors a reliable way of identifying and direct treatment. By proving an objective way, It helps make sure pain is noticed and taken seriously. The quality of care is improved due to helping healthcare providers in assessing pain in the same manner. The score of pain scale guarantees that pain is identified and addressed for even ate patients that are most at risk.
Components of CPOT
• Facial Expression: Looks at the patient’s face to see if they are relaxed, frowning, or grimacing.
• Body Movements: Checks if the patient is calm, restless, or moving in a way that shows discomfort.
• Muscle Tension: Feels if the patient’s muscles are relaxed, stiff, or very tight.
• Compliance with Ventilator (or Vocalization): For patients on a ventilator, it checks if they are going along with the machine or fighting against it. For those not intubated, it looks at sounds like groaning, crying, or moaning.
Advantages of CPOT Scale?
The Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) provides a reliable and careful way of evaluating pain in non-verbal intensive care unit patients. Compared to other tools, it is more precise since it tracks specific factors such as ventilator compliance and muscular tension. CPOT has been evaluated especially for adult patients in critical care, has shown sensitivity and reliability in various intensive care unit conditions, and improves patient outcomes by directing greater pain management.
The CPOT makes sure that even the most vulnerable patients have their pain noticed and treated. Critical care pain observation tool guarantees that patients in critical condition obtain prompt and suitable pain management, enhancing their comfort and the right time for recuperation.
Limitations of CPOT
The Critical-Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) is very accurate and useful tool but it has some limitations. The result can be different because it can be calculated by different doctors and this can be lead to inconsistency in the scrore. Since it was primarily created for adults, it may be less accurate in patients with severe neurological conditions, heavy sedation, facial paralysis, or in young patients.
It might be difficult to implement the tool as it requires the right resources and training. Also, nothing is known about how well it works for certain patient, like those with delirium. In complicated medical situations where several factors affect patient behavior, its accuracy may also be impacted.
Explore More Helpful Health Tools
Our website is here to create tools that help people to make better life choices and having your body and mind in control. We provide a range of health related tools like the CPOT Score Calculator designed to support your well-being.
Below you will find a couple of them and much more that are just a search away . If you don’t find any specific test or calculator you’re looking for please feel free to contact-us so we can create it for everyone.
COPD Assessment Test (CAT)
A short, validated 8-item questionnaire completed by COPD patients to evaluate how much the disease impacts their daily health status.
Caprini Score (2005) for VTE
A scoring system that adds up risk factors to estimate a patient’s chance of blood clots after surgery.