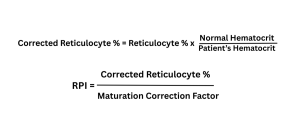
Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage – Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI)
The Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage / Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI) is used to assess bone marrow response in patients with anemia. It helps clinicians determine whether the marrow is producing red blood cells adequately and guides the evaluation of different types of anemia. Accurate RPI calculation is essential for diagnosing and managing anemia effectively.
Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage calculator is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider.
Introduction to Reticulocytes
Before developing into erythrocytes, immature red blood cells called reticulocytes leave from the bone marrow. Under some stains, they still have remained RNA, which gives them a characteristic net-like look. Red blood cell generation and bone marrow function are reflected in reticulocyte counts. High reticulocyte counts may mean an increase in production related to the reaction to hemolysis or blood loss. While, low reticulocyte counts may point to anemia or marrow malfunction.
Reticulocyte counts is very important in healthcare since they show how quickly the body is reacting in producing new red blood cells. For doctors in necessary to know the count because it give them the necessary info, such as how good the bone narrow is working and how is the body reacting to problems that affect red blood production like anemia. Sophisticated measurements helps them to utilize and evaluate iron status and track the efficacy of treatment.
Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage/ Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI)
In order to properly compensate for the severity of anemia and the extended maturation period of reticulocytes in the blood, the raw reticulocyte count is adjusted to calculate the Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage, or RPI. It provides a better view of red blood cell creation and bone marrow function. While bone marrow generates more reticulocytes in anemia, an obvious proportion could be inaccurate. The RPI indicates if the bone marrow is reacting properly by adjusting the value with the patient’s hematocrit. Corrected Reticulocyte Percentage is useful way in diagnosing different kinds of anemia and in evaluating bone narrow functioning.
Clinical Uses of Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI)
RPI or also referenced as reticulocyte count is measurement used in determining the bone narrow response to anemia. This measurement provides a more precise and accurate evaluation of red blood cells production compared to basic reticulocyte count. Reticulocyte Production Index is precise method because it takes into consideration the degree of anemia and the maturation period of reticulocytes.
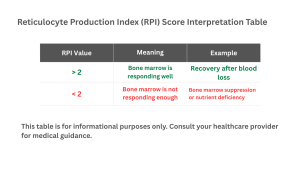
The RPI is useful because it helps doctors:
- Find the reason of your anemia: A high RPI indicates the body is losing or destroying blood cells, while a low RPI indicates the bone marrow isn’t producing enough of them.
- Choose a course of treatment: Such as using medication to increase the formation of red blood cells.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the treatments: Like following a blood transfusion or the use of particular medications.
- Calculate potential dangers to health: Particularly for those with chronic conditions like heart issues.
Limitations of RPI
The Reticulocyte Production Index (RPI) is helpful for checking bone marrow response to anemia, but it has some limits:
- Not reliable in children : it hasn’t been well tested or standardized for pediatric use.
- Affected by changes in plasma: illness such as renal illness or blood boosting may cause results to be less precise.
- Depends on precise testing: findings can be impacted by mistakes in maturation time or reticulocyte numbers.
- Different cut-offs & biases : Registry data may be unreliable, and studies may have different RPI cut-offs.
- Results can be altered by outside factors : such as ethnicity, genetics, and altitude.
- Standardization is required: laboratories must offer precise procedures and interpretation guidelines.
Explore More Helpful Health Tools
Our website is here to create tools that help people to make better life choices and having your body and mind in control. We provide a range of health related tools like the RPI Calculator designed to support your well-being.
Below you will find a couple of them and much more that are just a search away . If you don’t find any specific test or calculator you’re looking for please feel free to contact-us so we can create it for everyone.
Mean Arterial Pressure Calculator
Quickly calculate Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) to assess tissue perfusion and cardiovascular health.
Serum Anion Gap Calculator
Instantly compute the serum anion gap to help detect and interpret acid-base imbalances.